Organizing is the function of management which follows planning. It is a function in which the synchronization and combination of human, physical and financial resources takes place. All the three resources are important to get results. Therefore, organizational function helps in achievement of results which in fact is important for the functioning of a concern. According to Chester Barnard, “Organizing is a function by which the concern is able to define the role positions, the jobs related and the co-ordination between authority and responsibility. Hence, a manager always has to organize in order to get results.
It is a mechanism or structure that enables different groups of people to work together effectively.Organization establishes the pattern of relationship by giving duties and responsibilities to the individuals.It coordinates all the activities of individuals to achieve common goals of an enterprise.Proper organization facilitates the effective use of the manpower and easy administration.
Organizational Structure
An organizational structure consists of activities such as task allocation, coordination and supervision, which are directed towards the achievement of organizational aims. It can also be considered as the viewing glass or perspective through which individuals see their organization and its environment.
An organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs.Organizational structure affects organizational action in two big ways. First, it provides the foundation on which standard operating procedures and routines rest. Second, it determines which individuals get to participate in which decision-making processes, and thus to what extent their views shape the organization’s actions.
The structure of one industrial organization differs from that of another organisation and it depends upon
1.Size of the organization
2.Nature of the product being manufactured
3.Complexity of the problems being faced
Few commonly known types of organizational structures are
A manager performs organizing function with the help of following steps
1. Identification of activities - All the activities which have to be performed have to be identified first. For example,quality control, inventory control,recording information etc. All these activities have to be grouped and classified into units
- Organizing the activities - In this step, the manager tries to combine and group similar and related activities into units or departments. This organization of dividing the whole concern into independent units and departments is called departmentation.
- Classifying the authority - Once the departments are made, the manager likes to classify the powers and its extent to the managers. This activity of giving a rank in order to the managerial positions is called hierarchy. The top management is into formulation of policies, the middle level management into departmental supervision and lower level management into supervision of foremen. The clarification of authority help in bringing efficiency in the running of a concern. This helps in achieving efficiency in the running of a concern. This helps in avoiding wastage of time, money, effort, in avoidance of duplication or overlapping of efforts and this helps in bringing smoothness in a concern’s working.
- Co-ordination between authority and responsibility - Relationships are established among various groups to enable smooth interaction toward the achievment of the organizational goal. Each individual is made aware of his authority and he/she knows whom they have to take orders from and to whom they are accountable and to whom they have to report. A clear organizational structure is drawn and all the employees are made aware of it.
It is a mechanism or structure that enables different groups of people to work together effectively.Organization establishes the pattern of relationship by giving duties and responsibilities to the individuals.It coordinates all the activities of individuals to achieve common goals of an enterprise.Proper organization facilitates the effective use of the manpower and easy administration.
Organizational Structure
An organizational structure consists of activities such as task allocation, coordination and supervision, which are directed towards the achievement of organizational aims. It can also be considered as the viewing glass or perspective through which individuals see their organization and its environment.
An organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs.Organizational structure affects organizational action in two big ways. First, it provides the foundation on which standard operating procedures and routines rest. Second, it determines which individuals get to participate in which decision-making processes, and thus to what extent their views shape the organization’s actions.
The structure of one industrial organization differs from that of another organisation and it depends upon
1.Size of the organization
2.Nature of the product being manufactured
3.Complexity of the problems being faced
Few commonly known types of organizational structures are
- Line
- Functional
- Line and Staff
- Matrix
It is the most oldest and simplest method of administrative organization. According to this type of organization, the authority flows from top to bottom in a concern. The line of command is carried out from top to bottom. This is the reason for calling this organization as scalar organization which means scalar chain of command is a part and parcel of this type of administrative organization. In this type of organization, the line of command flows on an even basis without any gaps in communication and co- ordination taking place.
Merits
- Simplest
- Unity of Command
- Better discipline
- Fixed responsibility
- Flexibility
- Prompt decision
- Over reliance
- Lack of specialization
- Inadequate communication.
- Lack of Co-ordination
- Authority leadership
Functional Organization
It has been divided to put the specialists in the top position throughout the enterprise. This is an organization in which we can define as a system in which functional department are created to deal with the problems of business at various levels. Functional authority remains confined to functional guidance to different departments. This helps in maintaining quality and uniformity of performance of different functions throughout the enterprise.
Merits
- Specialization
- Effective Control
- Efficiency
- Expansion
- Lack of co-ordination
- Conflicts
- High costs
- Difficult in fixing responsibility
Line and Staff Organization
Line and staff organization is a modification of line organization and it is more complex than line organization. According to this organization, specialized and supportive activities are attached to the line of command by appointing staff supervisors and staff specialists who are attached to the line authority. The power of command always remains with the line executives and staff supervisors guide, advice and council the line executives.
Merits
- Expert advice
- Better co-ordination
- Training
- Unity of Action
- Balanced decisions
Demerits
- Assumption of authority
- Line and Staff conflicts
- Lack of sound advice
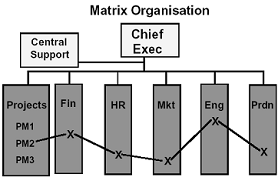
Matrix Organization
In matrix organization people who have similar skills will be gathered together to work on particular assignments. So for instance, all engineers may be working within one particular engineering department, and be under the same management - but these engineers will no doubt be assigned to a number of different projects, and have to report to different project managers during the process of completing the project. Hence, every engineer within the workplace will have to work under a number of different managers in order to get their own particular job done.
Merits
- Development of skills
- Higher Efficiency
- Optimum utilization of resources
- Better decisions
Demerits
- Increase in workload
- High operational cost
- Absence of unity of command
- Complexity
Importance of Organizational Structure
Organization structure is like the framework of an organization. Organizational structures imply formal relationships with well defined duties and responsibilities. It also implies to the hierarchical relationships between superior and subordinates within the organization. It helps in coordinating various tasks and activities that are assigned to different persons and departments. Organizational structure helps in having set of policies, procedures, standards and methods of evaluation of employee’s performance. It should be developed as per needs of the people in the organization.
To conclude I can say that Organizational structure plays significant role in effective and efficient functioning of organization.